Exploring ChatGPT for
Quest Systems in Unity
Demo Video
Overview
We explored whether Large Language Models (LLMs), specifically ChatGPT, could replace traditional quest systems in games. Using a Unity prototype, we integrated ChatGPT through its API and conducted over 3,600 automated trials across multiple models and settings. Our findings highlight LLMs’ strong potential for rapid prototyping but reveal critical limitations in reliability and scalability.
My Role
Designed Unity API integration
Built automated test scripts for large-scale evaluation
Analyzed results & co-authored empirical analysis section
Tools Used
Unity (C#)
OpenAI API
Automated Testing Framework
Prototype Setup
The prototype scene included interactive objects with condition states (e.g., Broken/Fixed, Dirty/Clean). ChatGPT generated quests instructing the player to change object states, allowing us to test reliability of structured outputs.
Methodology
To evaluate ChatGPT’s potential as a quest generator, we designed a series of automated tests in Unity.
Objects & States: Ran trials with 10 and 50 objects, each with either 2 or 5 possible states (e.g., Fixed/Broken, Dirty/Clean).
Models Tested: ChatGPT-4.1 Normal, Mini, and Nano.
Temperature Values: 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, and 2.0.
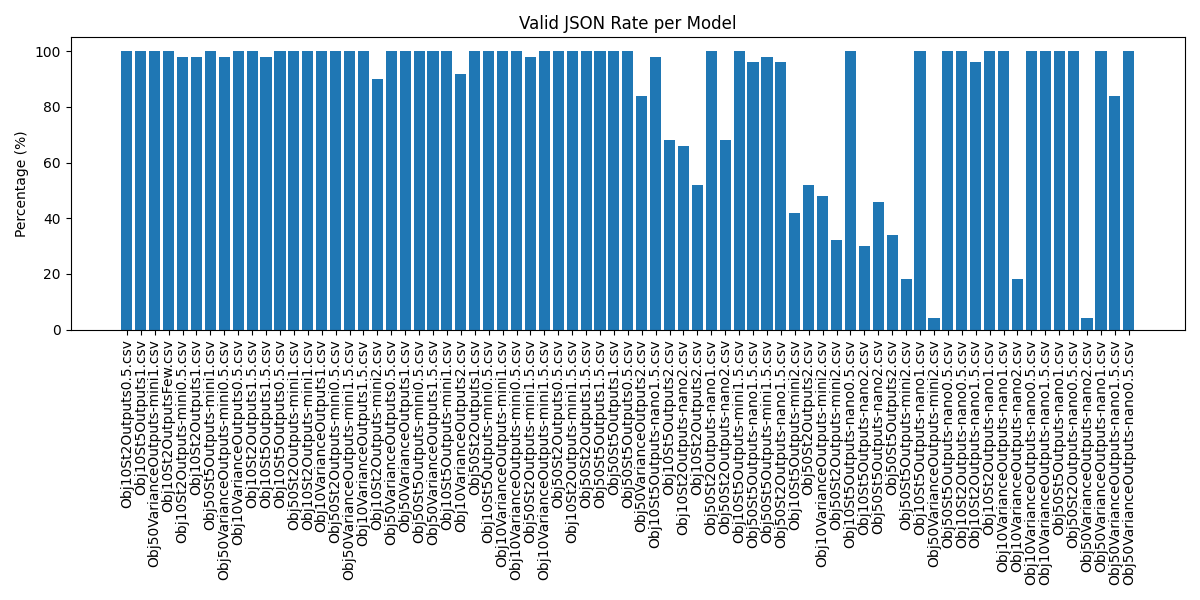
Testing Scale: Over 3,600 automated trials were conducted to measure reliability and variance in responses.
Each test checked whether the model returned valid JSON, adhered to the required schema, avoided hallucinations, and produced usable quest instructions.
Unity Scene State
Prompt to ChatGPT
JSON Response
Quest Displayed in Game
Results
Our testing revealed clear differences between models and configurations:
GPT-4.1 Normal was the most reliable, averaging ~73% success across trials.
GPT-4.1 Mini performed reasonably well on simpler tasks, but reliability dropped sharply with more objects and states.
GPT-4.1 Nano frequently failed schema compliance, often hallucinating objects or returning unusable responses.
Key statistics across all trials:
Valid JSON: 86%
Schema Compliance: 62%
No Hallucinations: 53%
Fully Passed (all criteria met): 53%
Takeaways and Conclusion
LLMs can be a powerful tool for rapid prototyping and experimentation in games.
Current models are not yet reliable enough for production use in structured systems like quests.
Developers must apply schema validation, guardrails, and temperature control to make outputs usable.
Smaller models (like Nano) are unsuitable for structured pipelines, while larger models (Normal) show potential if constraints are applied.
This project highlights both the promise and limitations of using LLMs for quest generation in Unity. While ChatGPT can successfully create structured quests and speed up prototyping, its reliability issues make it unsuitable as a direct replacement for traditional quest systems. Future improvements to model accuracy, combined with robust validation layers, could unlock new opportunities for integrating AI-driven content generation into games.
Resources